Jenkins Basics
Install Jenkins Open Command Prompt and Type"java -jar path of jenkins.war file" Create account Use "http://localhost:8080" to access jenkins Steps To Demo Jenkins 1)Create Test Project 1a)Right click on java file and TestNG->Convert to TestNG 2)open cmd and go to project folder ex. cd C:\AndroidDemoworkspace\JenkinsAppium 3)Set Classpath ex. set classpath=C:\AndroidDemoworkspace\JenkinsAppium\lib\*;C:\AndroidDemoworkspace\JenkinsAppium\bin; 4)Run Test ex. java org.testng.TestNG testngappium.xml and Check Test Script working or not. 5)Create batch file . Open notepad file -> enter "java -cp bin;lib/* org.testng.TestNG testngappium.xml" and save as "run.bat" 6)Open Jenkins console and login 7)Create new job. Click on Item ->Name of Item, select freestyle project and save it 8)Click on advanced setting and tick custom workspace and enter project path ex. C:\AndroidDemoworkspace\JenkinsAppium, select build with execute Windows batch file , apply and Save it. 9)Build now and click on build history ->console , We will get output Note:- No UI appears while executing Test case ex browser actions
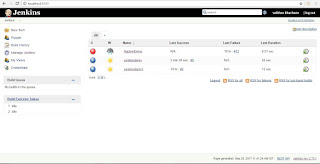
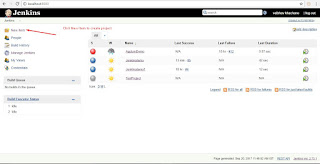
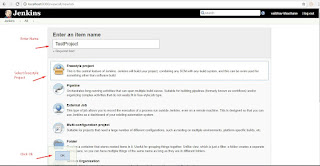
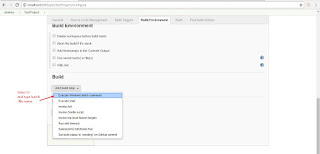
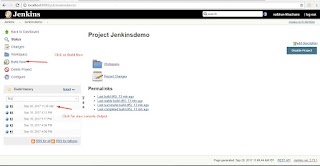
Run Test through command Line
cd C:\AbcAutomation\AbcTestJenkin // set our Project location
set classpath=C:\AbcAutomation\AbcTestJenkin\lib\*;C:\AbcAutomation\AbcTestJenkin\bin\example\*;
\\ set lib and bin folder path
java -cp bin;lib/* org.testng.TestNG testng.xml //execute testng file of project
IPhone and IPad Resolutions (IPhone 8, 8 Plus and IPhone X)
Device Portrait dimensions Landscape dimensions 12.9" iPad Pro 2048px × 2732px 2732px × 2048px 10.5" iPad Pro 1668px × 2224px 2224px × 1668px 9.7" iPad 1536px × 2048px 2048px × 1536px 7.9" iPad mini 4 1536px × 2048px 2048px × 1536px iPhone X 1125px × 2436px 2436px × 1125px iPhone 8 Plus 1242px × 2208px 2208px × 1242px iPhone 8 750px × 1334px 1334px × 750px iPhone 7 Plus 1242px × 2208px 2208px × 1242px iPhone 7 750px × 1334px 1334px × 750px iPhone 6s Plus 1242px × 2208px 2208px × 1242px iPhone 6s 750px × 1334px 1334px × 750px iPhone SE 640px × 1136px 1136px × 640px
Android Globalization Best Practices
First, what is Globalization? Globalization, also referred to as Internationalization or the i18n standard; is the process of designing a software application so that it can potentially be adapted to various languages and regions without engineering changes. It's a process that affects how you engineer the UX, UI and code of your application. It's not an easy process to cover all aspects, but once you get your application guidelines right, and build your design and engineering processes around it, you should be able to pull it through. What about Localization? Localization; also referred to as i10n, is different from Globalization. Localization requires you to add appropriate resources to your software to ensure that a given country, locale, language, or culture is supported. Or, its the process of adding another language to your app, which is hopefully designed for i18n! All Text Must be Resource Based Well, this is a basic thing, but it is important to highlight. Don't hardcode any strings either in your screen layouts nor in your application code; strings.xml is a key artifact in your application. If you mistakenly hardcode strings, it will be a costly process to fix. Android Studio will warn you if you leave a string hardcoded, but I prefer to treat these as errors and log an issue when one is detected and fix prior to a release. This is a common pitfall that designers fall in. We usually design our layouts with a single language in mind; typically English, and assume that translations will fall into place; Unfortunately, not all languages are equal. You should always allow extra space in your layout for text to grow and shrink based on the language translation. Perhaps leave a 40-50% space to cater for that. In some cases, you might have to create separate layouts to cater for extreme cases. The IBM Globalization Guidelines page has a good table that compares text size increase when translating from English. Number of Characters in Text Additional Physical Space Required Up to 10 100% to 200% 11 to 20 80% to 100% 21 to 30 60% to 80% 31 to 50 40% to 60% 51 to 70 31% to 40% Over 70 30% This calculation is based on the number of characters in the text string and includes the spaces and punctuation marks within the string. For example, the string "Hello World!" contains twelve characters. Add Comments to String Resources There are many cases where strings we use make sense in a one language but can't be translated directly to other languages. Especially if we use playful terms. In these cases, ensure your resource file has comments on the context of the messages to help your translators better understand the message you need to convey and provide proper translations in the target language; whether in a localized playful manner, or a more standard language. Never, Ever Concatenate We tend to fall into the temptation of concatenating strings to build dynamic messages, and we forget that word ordering is different across languages. Whether we are adding user names, amounts, we should always use string formatting. Use Proper Plural Strings Don't try to build your quantity/amount texts in code by assigning plural nouns based on the value you have, as different languages will have different ways of representing amounts and quantities. So if you are trying to say: I ate 3 cookies, don't use the following resource strings Handle Dates Properly Date formats vary across cultures, so make sure that your application uses the correct format for handling dates by using the DateUtils and DateFormat classes. Don’t use hardcoded date formats such as MM/dd/yyyy, you’ll just confuse everyone. You can use DateUtils to show a relative timespan string It’s not only display that needs to be catered for. When you accept date values from users, or try to capture stamps, make sure you convert them to a standard culture-neutral format prior to storage. Otherwise, you won’t be able to analyze or render properly if a user switches cultures. Dynamic Formatting When you need to format or highlight part of the text you are showing (color, weight, etc.) don’t use index to manipulate a ForegroundColorSpan. This will get you in trouble with translated strings. Use HTML formatting instead within your resource strings.Colors This is a frequently missed one. Colors have different meanings in different cultures. For example, while Green is used to indicate positive increase or trend; like in a stock price, in China, Red is used for that. You should also cater for this and support different colors for different cultures.
Mobile Automation using Appium and Java (Page Objects)
********************************Main Test File:-*************************************************************
package com.example;
import io.appium.java_client.android.AndroidDriver;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.DesiredCapabilities;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.ExpectedConditions;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.WebDriverWait;
import org.testng.Assert;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterTest;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeTest;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import com.example.pages.HannaPagesTest;
public class HannaTest
{
AndroidDriver driver;
@BeforeTest
public void setUp() throws MalformedURLException
{
DesiredCapabilities capabilities = new DesiredCapabilities();
capabilities.setCapability("deviceName", "ZX1B32FFXF");
capabilities.setCapability("appPackage", "com.hannainst.hannalab");
capabilities.setCapability("appActivity","com.hannainst.hannalab.ManagerActivity");
driver = new AndroidDriver(new URL("http://127.0.0.1:4723/wd/hub"), capabilities);
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
WebDriverWait wait = new WebDriverWait(driver, 300);
wait.until(ExpectedConditions.elementToBeClickable(By.className("android.widget.RelativeLayout")));
}
@Test(priority = 0)
public void checkAppElementPresent()
{
HannaPagesTest hanna=new HannaPagesTest(driver);
if(hanna.verifyResult1("No Probe Connected"))
System.out.println("App Launch TC Passed");
else
System.out.println("App Launch TC Failed");
}
@Test(priority = 1)
public void CheckAppVersion()
{
HannaPagesTest hanna=new HannaPagesTest(driver);
if(hanna.verifyResult2("Version 2.0.0 Beta"))
System.out.println("App Version TC Passed");
else
System.out.println("App Version TC Failed");
}
@AfterTest
public void End() throws IOException
{
//driver.removeApp("com.hannainst.hannalab");
driver.resetApp();
driver.quit();
//driver.close();
}
}
************************Page Object Test File************************************
package com.example.pages;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.PageFactory;
import io.appium.java_client.android.AndroidDriver;
import io.appium.java_client.pagefactory.AndroidFindBy;
import io.appium.java_client.pagefactory.AppiumFieldDecorator;
public class HannaPagesTest
{
public HannaPagesTest(AndroidDriver driver)
{
PageFactory.initElements( new AppiumFieldDecorator(driver), this);
}
@AndroidFindBy(name="No Probe Connected")
public static WebElement text1;
@AndroidFindBy(xpath="//*[@class='android.widget.ImageButton' and @content-desc='Navigate up']")
public static WebElement text2;
@AndroidFindBy(id="com.hannainst.hannalab:id/versionName")
public static WebElement text3;
public boolean verifyResult1(String result)
{
if(text1.getText().equals(result))
return true;
else
return false;
}
public boolean verifyResult2(String result)
{
text2.click();
if(text3.getText().equals(result))
return true;
else
return false;
}
}
***************************************************************************************************************************
Regression Testing Tips for selecting Test Cases
Regression testing is selective retesting of a system or component to verify that modifications have not
caused unintended effects in previously working modules of software/application. This type of testing is
typically associated either as a ‘challenge’ or ‘unimportant’ by developers; but a good tester always enjoys
breaking the software to scour out each and every fault from it. Having said that even regression testing
can become a challenge for the testers as well. Here are some of the reasons:-
1. The Number of test cases in regression suite increases with each new feature.
2. Sometimes, the execution of entire regression test suite becomes difficult due to time and budget constraints.
3. Minimizing test suite while achieving maximum test coverage is not a cake walk.
4. Determination of frequency of Regression Tests after every modification or every build update or after a
bunch of bug fixes is always a challenge.
The graph below depicts the same
 Hence selecting test cases for regression testing is quite a tricky task. Today, I am sharing some tips that
I found to be most effective while selecting test cases for regression testing
Below are tips:-
1. Include the test cases which have frequent defects:
Some areas in product are so error prone that they usually fail with a small change in code. We can keep track
of failing test cases due to such areas throughout the product cycle and cover them in regression test suite.
2. Include the test cases which verify core features of the product:
Prior to designing of the test cases figure out all core features of application. Ensure that, test case cover
all functionality mentioned in requirement document. One can make use of traceability matrix to make sure that
no requirement is left untested.
Example:- Client would never expect a Home Page/Login Page/Key functionalities of his application getting failed.
3. Include the test cases for Functionalities which have undergone more and recent changes:-
SRS keeps on getting updated. Sometimes, the updates are not in full change to the previous SRS. But to some extent
(may be 15-30 %) changes may happen for every version upgrade. We testers have to agree that, it’s difficult to
keep writing (modifying) test cases, as the SRS keeps on getting updated often and this leads to some end moment
internal defects and changes into the code which in turn might break some already existing functionalities,
So it’s a “Must” (a must with capital M ) to always include such test cases which has recent changes.
4. Include all the Integration test Cases:
Even if Integration testing is a separate part of software testing cycle, its test cases should be included
in regression test suite.
A last moment fix, in already tested application can break the integrity between different modules. For
example, data might get lost across an interface, messages might not get passed properly or interfaces might not be
implemented as specified.
5. Include all Complex Test Cases:-
Some functionality of the system may only be accomplished by following some complex sequence of GUI events.
For example, to open a file a user may have to click on the File Menu and then select the Open operation,
and then use a dialog box to specify the file name, and then focus the application on the newly opened
window. Obviously, increasing the number of possible operations increases the sequencing problem exponentially.
This can become a serious issue even if one of the steps is not working—A whole functionality comes to HALT,
and End-User feels like a crap . That’s why all such complex test case should be included in regression test suite.
6. Prioritize the test cases for regression testing:
Prioritize the test cases depending on business impact, critical & frequently used functionalities. It is always
helpful if some analysis is done to find out what test cases are relevant and what are not. It is a good approach
to plan and act for regression testing from the beginning of project before the test cycles. One of the ideas is
to classify the test cases into various Priorities based on importance and customer usage. Here it is suggested
the test cases be classified into three categories:-
Hence selecting test cases for regression testing is quite a tricky task. Today, I am sharing some tips that
I found to be most effective while selecting test cases for regression testing
Below are tips:-
1. Include the test cases which have frequent defects:
Some areas in product are so error prone that they usually fail with a small change in code. We can keep track
of failing test cases due to such areas throughout the product cycle and cover them in regression test suite.
2. Include the test cases which verify core features of the product:
Prior to designing of the test cases figure out all core features of application. Ensure that, test case cover
all functionality mentioned in requirement document. One can make use of traceability matrix to make sure that
no requirement is left untested.
Example:- Client would never expect a Home Page/Login Page/Key functionalities of his application getting failed.
3. Include the test cases for Functionalities which have undergone more and recent changes:-
SRS keeps on getting updated. Sometimes, the updates are not in full change to the previous SRS. But to some extent
(may be 15-30 %) changes may happen for every version upgrade. We testers have to agree that, it’s difficult to
keep writing (modifying) test cases, as the SRS keeps on getting updated often and this leads to some end moment
internal defects and changes into the code which in turn might break some already existing functionalities,
So it’s a “Must” (a must with capital M ) to always include such test cases which has recent changes.
4. Include all the Integration test Cases:
Even if Integration testing is a separate part of software testing cycle, its test cases should be included
in regression test suite.
A last moment fix, in already tested application can break the integrity between different modules. For
example, data might get lost across an interface, messages might not get passed properly or interfaces might not be
implemented as specified.
5. Include all Complex Test Cases:-
Some functionality of the system may only be accomplished by following some complex sequence of GUI events.
For example, to open a file a user may have to click on the File Menu and then select the Open operation,
and then use a dialog box to specify the file name, and then focus the application on the newly opened
window. Obviously, increasing the number of possible operations increases the sequencing problem exponentially.
This can become a serious issue even if one of the steps is not working—A whole functionality comes to HALT,
and End-User feels like a crap . That’s why all such complex test case should be included in regression test suite.
6. Prioritize the test cases for regression testing:
Prioritize the test cases depending on business impact, critical & frequently used functionalities. It is always
helpful if some analysis is done to find out what test cases are relevant and what are not. It is a good approach
to plan and act for regression testing from the beginning of project before the test cycles. One of the ideas is
to classify the test cases into various Priorities based on importance and customer usage. Here it is suggested
the test cases be classified into three categories:-
| Priority-0 | Priority-1 | Priority-2 |
|---|---|---|
| Sanity test cases which checks basic functionality(as per the SRS of product) and are run for pre-system acceptance and when product goes through major change. These test cases deliver a very high project value to both engineers and to customers. | This includes the test cases which tests essential functionalities that deliver high project value to both engineers and customers. | These are executed as a part of ST cycle and selected for regression testing on need basis. These test cases deliver moderate project value. |
Difference between xcworkspace and xcodeproj
xcworkspace :- Is generated when project includes external libraries(dependency clasess)and clasess,When its generated afterwards use this file to execute our project xcodeproj :- Is the default executable file of the project
iOS Split View Supported devices
Device |
Slide Over |
Picture in Picture |
Split View |
|---|---|---|---|
|
iPad mini 2 |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
iPad mini 3 |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
iPad mini 4 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
iPad Air |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
iPad Air 2 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
iPad Pro |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Splitview screen dividation
Landscape Portrait
66-33 66-33
50-50
Ipad Air Splitview(2/3) Landcape
Ipad Air Splitview(1/3) Landcape
Ipad Air Splitview(1/2) Landscape
Ipad Air Splitview(2/3) Portrait
Ipad Air Splitview(1/3) Portrait
Apple Ref document for split view
Challenges of iOS app development
- Challenge 1 – Navigation Panel in the Developer Portal The navigation panel could be complicated for those who are fresh into iOS application development. The more the iPhone developers use this portal the more easily they will be able to navigate. Just make sure that you have a prior knowledge about the portal.
- Challenge 2 – iOS Application Compatibility There are various Apple products available in the market today including iPhone 4, 4S, 5, 5S, 1st, 2nd, 3rd Generation iPad Mini series and the iPad Air so it is extremely necessary for an excellent iOS platform app to be compatible with all these products. Testing an application becomes highly important so that it can run smoothly thereby using TaaS product like Testelf or TestFlight can aid through this issue.
- Challenge 3 – Beta Users Testing The best way for any application to be known and accepted amongst the consumers is allowing tests to be done through Beta users. They will be able to help you identify the possible failure conditions specific to your developed application. One such solution is testflightapp.com which comes handy for beta testing your app on the go.
- Challenge 4 – Apple App Store Approval It is very necessary to know about the App Store guidelines before you start developing an iOS based application. One must conform to all the listed rules and regulations so that your app gets approved in the App Store. This will save your time and aid you through various investment challenges.
- Challenge 5 – Poor Network Conditions The speed that you are using might not be the speed that your end consumer may be using. So it becomes highly essential that you pass your iOS app through a test done by the Network Link Conditioner which will help you in invigorating not up to the mark networks.
Challenges of Android app development
Some key Android app development challenges are listed below:
- Software Fragmentation: There are many Android OS versions which developers find hard to keep up with . when it comes to app development. It is impractical to focus only on the most recent Android version as not all users may have upgraded to the most recent OS.
- Hardware Fragmentation: This becomes a big Android app development challenge since there are nearly 170+ devices running the OS. Each device has different features with respect to keyboard forms, screen size, camera buttons, etc., making it a development nightmare.
- No Software/Hardware Standardization: The huge number of devices running Android gives rise to another Android app development challenge–lack of software/hardware standardization across the devices. This becomes a nightmare for developers as each device has a different function for a different button.
- Several Carriers: Android app development service providers should know that there are many carriers available for the Android OS, each with the freedom to modify the OS for their purposes. This only multiplies the fragmentation problems for developers.
- Security:Unlike Apple’s strict guidelines for app development, no such governance exists for Android apps. As a result, many malware problems arise and software/hardware fragmentation only makes fixing the problems more difficult. This gives rise to tremendous amounts of security issues.
- Market Research Costs: One of the biggest Android app development challenges for developers is the cost behind market research. Understanding the end user is key to Android app development, but can require a lot of research, making it costly for developers.
- Patent Issues: The recent lawsuits indicate that several Android features may be declared as violation of patent issues. This can become a big Android app development challenge for developers.
- Android Market Search Engine: One of the major Android app development challenges for developers is the Android marketplace. Android has more than 8 million apps on its marketplace today and getting your app visible amongst them is a challenge. As a result, even with a great android app developed, if you don’t pay attention to its promotion, you may lose out on gaining any traction.
Xcode and MAC OS versions
Latest xcode and MAC OS X verison history
macOS 10.12
Xcode 8.2.1
Xcode 8.2
Xcode 8.1
OS X 10.11
Xcode 8.2.1
Xcode 8.2
Xcode 8.1
Xcode 8.0
Xcode 7.3.1
Xcode 7.2.1
OS X 10.11
Xcode 7.2.1
Xcode 7.0
Xcode 6.4
Xcode 6.3.1
Xcode 6.3
Xcode 6.2
Xcode 6.1.1
Xcode 6.1
OS X 10.9
Xcode 6.2
Xcode 5.1.1
Xcode 5.1
Xcode 5.0.2
Xcode 5.0.1
Android Versions Comparisn
| Version name | Key user features added | Key developer features added | Release date | Android market share | API Level | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Android 7.1 | Nougat |
|
| 2016-10-04 | 0.2 % | 25 |
| Android 7.0 | Nougat |
|
| 2016-08-22 | 0.5 % | 24 |
| Android 6.0.1 | Marshmallow | New emojis | 2015-12-07 | 29.6 % (6 - 6.0.1) | 23 | |
| Android 6 | Marshmallow |
|
| 2015-10-05 | 29.6 % (6 - 6.0.1) | 23 |
| Android 5.1.1 | Lollipop |
| 2015-04-21 | 23.3 % (5.1 - 5.1.1) | 22 | |
| Android 5.1 | Lollipop |
| 2015-03-09 | 23.3 % (5.1 - 5.1.1) | 22 | |
| Android 5.0.2 | Lollipop |
| 2014-12-19 | 10.1 % (5.0 - 5.0.2) | 21 | |
| Android 5.0.1 | Lollipop |
| 2014-12-02 | 10.1 % (5.0 - 5.0.2) | 21 | |
| Android 5.0 | Lollipop |
|
| 2014-10-17 | 10.1 % (5.0 - 5.0.2) | 21 |
| Android 4.4.4 | KitKat |
| 2014-06-23 | 22.6 % (4.4 - 4.4.4) | 19 | |
| Android 4.4.3 | KitKat |
| 2014-04-14 | 22.6 % (4.4 - 4.4.4) | 19 | |
| Android 4.4.2 | KitKat |
| 2013-12-09 | 22.6 % (4.4 - 4.4.4) | 19 | |
| Android 4.4.1 | KitKat |
| 2013-12-05 | 22.6 % (4.4 - 4.4.4) | 19 | |
| Android 4.4 | KitKat |
|
| 2013-10-31 | 22.6 % (4.4 - 4.4.4) | 19 |
| Android 4.3 | Jelly Bean |
|
| 2013-07-24 | 1.7 % (4.3) | 18 |
| Android 4.2.2 | Jelly Bean |
|
| 2013-02-11 | 5.9 % (4.2 - 4.2.2) | 17 |
| Android 4.2.1 | Jelly Bean |
| 2012-11-27 | 5.9 % (4.2 - 4.2.2) | 17 | |
| Android 4.2 | Jelly Bean |
|
| 2012-11-13 | 5.9 % (4.2 - 4.2.2) | 17 |
| Android 4.1.2 | Jelly Bean |
| 2012-10-09 | 4 % (4.1 - 4.1.2) | 16 | |
| Android 4.1.1 | Jelly Bean |
| 2012-07-23 | 4 % (4.1 - 4.1.2) | 16 | |
| Android 4.1 | Jelly Bean |
|
| 2012-07-09 | 4 % (4.1 - 4.1.2) | 16 |
| Android 4.0.4 | Ice Cream Sandwich |
| 2012-03-28 | 1.1 % (4.0.3 - 4.0.4) | 15 | |
| Android 3.2.6 | Honeycomb | Minor fixes | 2012-02-15 | 0 % | 13 | |
| Android 4.0.3 | Ice Cream Sandwich |
| 2011-12-16 | 1.1 % (4.0.3 - 4.0.4) | 15 | |
| Android 3.2.4 | Honeycomb | Added "Pay as you go" for tablets | 2011-12-15 | 0 % | 13 | |
| Android 4.0.2 | Ice Cream Sandwich | Minor fixes | 2011-11-28 | 0 % | 14 | |
| Android 4.0.1 | Ice Cream Sandwich |
| 2011-10-19 | 0 % | 14 | |
| Android 4.0 | Ice Cream Sandwich |
|
| 2011-10-18 | 0 % | 14 |
| Android 3.2.2 | Honeycomb | Minor fixes | 2011-09-30 | 0 % | 13 | |
| Android 2.3.7 | Gingerbread |
| 2011-09-21 | 1 % (2.3.3 - 2.3.7) | 10 | |
| Android 3.2.1 | Honeycomb |
| 2011-09-20 | 0 % | 13 | |
| Android 2.3.6 | Gingerbread |
| 2011-09-02 | 1 % (2.3.3 - 2.3.7) | 10 | |
| Android 2.3.5 | Gingerbread |
| 2011-07-25 | 1 % (2.3.3 - 2.3.7) | 10 | |
| Android 3.2 | Honeycomb |
|
| 2011-07-15 | 0 % | 13 |
| Android 2.3.4 | Gingerbread |
|
| 2011-05-10 | 1 % (2.3.3 - 2.3.7) | 10 |
| Android 3.1 | Honeycomb |
| 2011-05-10 | 0 % | 12 | |
| Android 3.0 | Honeycomb |
|
| 2011-02-22 | 0 % | 11 |
| Android 2.3.3 | Gingerbread |
| 2011-02-09 | 1 % (2.3.3 - 2.3.7) | 10 | |
| Android 2.3 | Gingerbread |
|
| 2010-12-06 | 0 % (2.3 - 2.3.2) | 9 |
| Android 2.2 | Froyo |
| 2010-05-20 | 0 % (2.2) | 8 | |
| Android 2.1 | Eclair |
| 2010-01-12 | 0 % | 7 | |
| Android 2.0.1 | Eclair | 2009-12-03 | 0 % | 6 | ||
| Android 2.0 | Eclair |
| 2009-10-26 | 0 % | 5 | |
| Android 1.6 | Donut |
| 2009-09-15 | 0 % | 4 | |
| Android 1.5 | Cupcake |
| 2009-04-30 | 0 % | 3 | |
| Android 1.1 | Banana bread |
| 2009-02-09 | 0 % | 2 | |
| Android 1.0 | Apple pie |
| 2008-09-23 | 0 % | 1 | |
| Android 0.9 | 2008-08-22 | 0 % |
How to create .ipa file
- How to create .ipa file
- .ipa file creation process
- How to create iOS provisioning certificate
STEP-1 1. Generating a Certificate Signing Request 2. Submitting a Certificate Signing Request for Approval 3. Approving Certificate Signing Requests 4. Downloading and Installing Development Certificates 5. Saving your Private Key and Transferring to other Systems I think if you read all this steps on the apple documentation at the given link then you don't need to refer to any other guide. STEP-2: Then just you need to download your certificates and provisioning profile. STEP-3: Just set the profile into your Project and Target Settings and then put proper Entitlements using "Entitlements.plist". STEP-4: Once you have done that, just set up your project in AdHoc Scheme. STEP-5: Clean your Project. STEP-6: Go to Product -> Click on Build For -> "Build For Archiving" STEP-7: Product -> Archive Now your Archive can be obtained in your Organizer where in you can save it to disk with an IPA extension and send it your client.
Agile Tester Principles
The principles we think are important for an agile tester are
1)Provide continuous feedback.
2)Deliver value to the customer.
3)Enable face-to-face communication.
4)Have courage.
5)Keep it simple.
6)Practice continuous improvement.
7)Respond to change.
8)Self-organize.
9)Focus on people.
10)Enjoy.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)

























